A) a decrease in sunspot activity and energy output from the Sun.
B) a decrease in snow and ice cover on Earth's surface.
C) a decrease in the amount of greenhouse gases.
D) a huge volcanic eruption that adds ash and dust to the atmosphere.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What happens to different isotopes of oxygen in this figure? 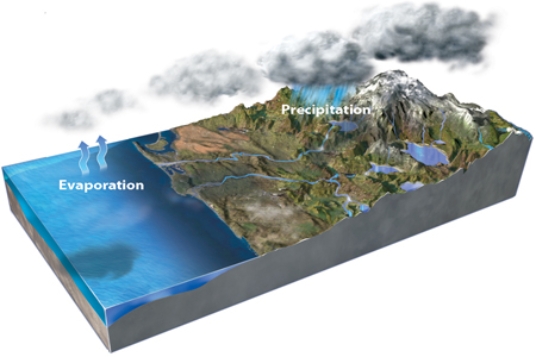
A) Evaporation concentrates lighter isotopes in the resulting water vapor.
B) Precipitation forms ice that is enriched in heavier isotopes relative to seawater.
C) Melting of ice preferentially releases heavier isotopes back into the ocean.
D) All of these.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the feature numbered 4 in the lower right of this figure? 
A) cirque
B) U-shaped valley
C) lateral moraine
D) terminal moraine
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How is a terminal or recessional moraine from a continental ice sheet typically expressed in the landscape?
A) as teardrop-shaped hills
B) as a series of small depressions, many of which are lakes
C) as a series of jagged ridges in the mountains
D) as a series of gently curved ridges
E) as hills that are smooth on one side and rough on the other side
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the amount of ice on the planet increased to the amount that was present during the last glacial maximum, how much would it cause global sea level to fall? If you do not remember the approximate size of this rise, the volume of additional ice is 52,000,000 km3 and the surface Area of the world's ocean is 361,000,000 km2.
A) less than 10 centimeters
B) 10 centimeters to 1 meter
C) 1 meter to 10 meters
D) 10 meters to 50 meters
E) more than 50 meters
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A geographic feature that formed as a result of the melting of the ice sheets during the Holocene Epoch is the
A) Great Lakes.
B) Mississippi River.
C) St.Lawrence River.
D) All of these.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which feature on this diagram is an arête? 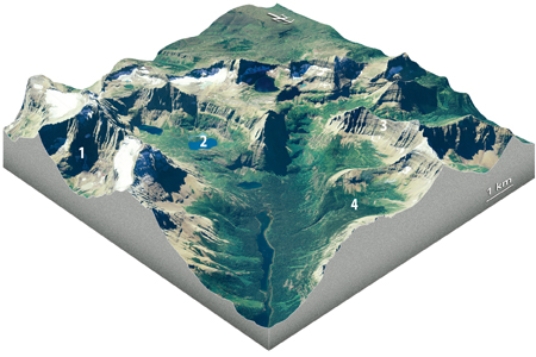
A) 1, the circular depression at the head of the valley
B) 2, a lake in the upper valley
C) 3, a steep ridge
D) 4, a valley that is above the level of the main valley
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which numbered feature(s) on this photograph are consistent with the presence of glaciers sometime in the past? 
A) 1, an arête
B) 2, U-shaped valley
C) 3, tarn
D) All of these.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the features labeled on this figure is a terminal or recessional moraine? 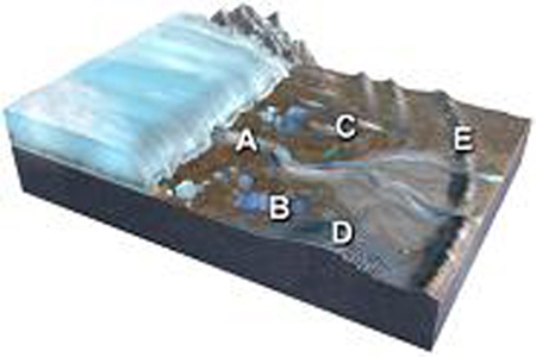
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the features labeled on this figure is a kettle? 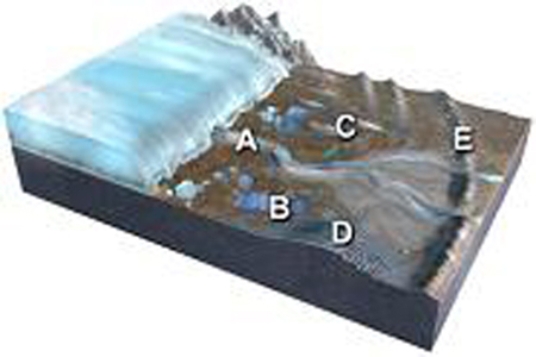
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What happens when a glacier encounters the sea or a lake?
A) The ice is denser than water and so scrapes along the bottom.
B) White icebergs float but blue icebergs sink to the bottom.
C) Large blocks of ice collapse off the front of the glacier and become icebergs.
D) Rocks released from melted icebergs float on the water surface.
E) All of these.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of glacier is shown in the center of this image? 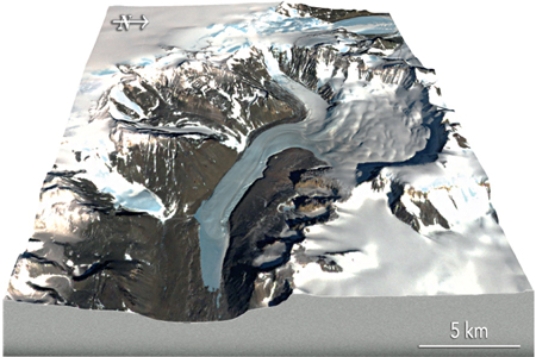
A) ribbon glacier
B) valley glacier
C) low-elevation glacier
D) high-elevation glacier
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The feature below has angular rocks on the outside and slowly flowing ice on the inside.It is called a(n) 
A) ice glacier.
B) nunatak.
C) cirque glacier.
D) rock glacier.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What do these curved ridges (eskers) suggest happened on the landscape? 
A) ancient shorelines were present
B) meltwater channels were below or within a glacier
C) soft glacial sediment was shaped by the moving glacier
D) glacially derived, wind-blown dust was abundant
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these areas is believed to have not been mostly by ice during thee last glacial maximum in the Pleistocene Epoch?
A) Ontario, Canada
B) Quebec, Canada
C) Alaska, United States
D) Michigan, United States
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The type of glacial debris that can fall into a crevasse is
A) supraglacial debris.
B) englacial debris.
C) subglacial debris.
D) All of these.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the photograph below, the ice must have flowed 
A) from the background into the foreground (i.e., out of the screen and toward you) .
B) from the foreground into the background (i.e., away from you as you are looking at it) .
C) from left to right.
D) from right to left.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Till is
A) sorted but not stratified.
B) stratified but not sorted.
C) sorted and stratified.
D) neither sorted nor stratified.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does a crevasse form?
A) A glacier moves over a volcanic hot spot, causing differential melting and caving it inward.
B) A glacier moves across a ridge of particularly resistant rock, which breaks the glacier from the bottom upward.
C) Internal stress causes a glacier's upper surface to break as the glacier moves.
D) A glacier moves over a pre-existing stream valley, which causes it to fracture on each side of the valley.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a way glaciers move downhill?
A) The glacier can slide over bedrock.
B) A glacier can move by internal shear and flow.
C) The upper parts of glaciers can fracture.
D) The lower part of a glacier flows faster than the upper part.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 77
Related Exams