A) Abnormal new bone formation
B) Avascular necrosis of bone
C) Focal lytic bone lesions
D) Generalized bone mineral loss
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 61-year-old woman comes to the clinic due to vision problems for the last 6 months. The patient says her eyes get tired easily, especially in the late afternoon and evening. She has smoked a pack of cigarettes daily for the past 35 years and does not use alcohol or illicit drugs. On physical examination, there is weakness of the extraocular muscles. Pupillary reflex, deep tendon reflexes, and sensation are normal. A contrast-enhanced CT scan of the chest is shown in the exhibit. 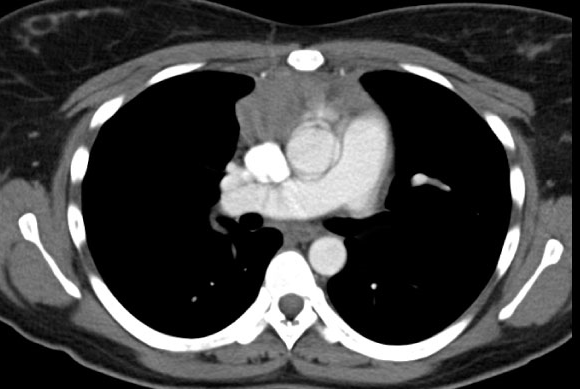 Which of the following is the most likely mechanism underlying this patient's symptoms?
Which of the following is the most likely mechanism underlying this patient's symptoms?
A) Antibodies against a neurotransmitter receptor
B) Antibodies against a presynaptic calcium channel
C) CD8+ lymphocyte-mediated nerve fiber demyelination
D) CD8+ lymphocyte-mediated skeletal muscle damage
E) Vascular deposition of circulating immune complexes
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 37-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to blood-tinged vomiting and abdominal discomfort. Six months ago, he lost his job as an investment banker and began drinking large amounts of whiskey on a daily basis. He has since been hospitalized several times with alcohol intoxication. His temperature is 36.7 C (98 F) , blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, pulse is 84/min, and respirations are 18/min. Physical examination shows a firm, enlarged liver. Peripheral blood smear results show neutrophils with 6-8 nuclear lobes. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for this patient's abnormal hematologic findings?
A) Blood lipid abnormality
B) Chronic blood loss
C) Cobalamin deficiency
D) Folate deficiency
E) Hypothyroidism
F) Myelodysplasia
H) C) and F)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 21-year-old man comes to the office due to multiple episodes of syncope. The patient has no chest discomfort or dyspnea. He has no known medical problems and does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. The patient is a computer analyst and leads a mostly sedentary lifestyle. He reports that several family members have died of sudden cardiac death. Genetic analysis reveals an ion channel defect. Due to the defect, cardiac cells show decreased outward potassium flow and resultant prolongation of the action potential. Which of the following is the most likely consequence of this patient's disease?
A) Abnormal anatomic communication between cardiac chambers
B) Asymmetric hypertrophy of the left ventricle
C) Ischemic myocardial necrosis followed by scarring
D) Left ventricular dilation and systolic dysfunction
E) Ventricular tachycardia and sudden death
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 45-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of severe chest pain, diaphoresis, and palpitations. The patient dies two hours after the onset of his symptoms. Autopsy reveals 100% occlusion of the left anterior descending artery. At the time of the patient's death, light microscopy of the affected myocardium would most likely demonstrate which of the following?
A) Edema and punctate hemorrhages
B) Myocyte hypereosinophilia
C) Dense interstitial neutrophil infiltrate
D) Extensive macrophage phagocytosis of the dead cells
E) Fibrovascular granulation tissue with neovascularization
F) Dense collagen scar
G) Normal myocardium
I) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 65-year-old man is found to have iron deficiency anemia. He has had no cough, abdominal pain, melena, or change in bowel habits but reports anorexia and a 5-kg (11-lb) weight loss in the past 2 months. Cardiopulmonary and abdominal examinations are unremarkable. Rectal examination shows guaiac-positive brown stool. A 3-cm mass is found on colonoscopy. Biopsy shows pleomorphic cells with large, dark nuclei forming irregular, crowded glands, some of which contain mucus. Imaging studies reveal multiple mass lesions in the liver and lungs. This patient's neoplasm most likely originated from which of the following locations?
A) Adrenal gland
B) Ascending colon
C) Lungs
D) Prostate
E) Rectosigmoid colon
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 35-year-old previously healthy man is brought to the emergency department after being involved in a motor vehicle collision. He was an unrestrained driver and hit his chest against the steering wheel during the collision. When the paramedics reached him, he reported chest discomfort but was hemodynamically stable. Shortly after arrival at the emergency department, the patient experiences worsening respiratory distress and becomes hypotensive. On physical examination, the patient appears anxious and is tachycardic and tachypneic. The trachea is midline; the jugular veins are distended. The anterior chest wall is bruised and tender to palpation. Vesicular breath sounds are present bilaterally. The abdomen is soft and nontender. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's clinical deterioration?
A) Aortic rupture
B) Cardiac tamponade
C) Diaphragmatic rupture
D) Hemothorax
E) Tension pneumothorax
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 14-year-old boy presents with nausea, vomiting, generalized headache, ataxia, and visual complaints. The headaches have awoken him nightly for the past six weeks. MRI reveals a cystic tumor in the cerebellum. Biopsy of the tumor reveals a well-differentiated neoplasm comprised of spindle cells that have hair-like glial processes and are associated with microcysts. These cells are mixed with Rosenthal fibers and granular eosinophilic bodies. Based on these findings, the most likely diagnosis is which of the following?
A) Pilocytic Astrocytoma
B) Glioblastoma multiforme
C) Medulloblastoma
D) Ependymoma
E) Neuroblastoma
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 56-year-old man is brought to the emergency department with new-onset tonic-clonic seizures. His past medical history is unremarkable. The patient recently has had right-sided headaches and has taken acetaminophen with some relief. MRI of the brain reveals several round lesions in the right temporal lobe. After initial evaluation, a stereotactic biopsy of one of the lesions is performed. The biopsy results show neoplastic tissue containing a mutation in the gene that encodes BRAF, a protein kinase. The point mutation results in a valine → glutamic acid substitution at position 600 of the protein. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A) Glioblastoma
B) Melanoma
C) Prostate cancer
D) Renal cell carcinoma
E) Small cell lung cancer
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 55-year-old man is admitted to the hospital due to abdominal discomfort and black stools. Medical history includes asthma and hypertriglyceridemia, for which the patient takes the appropriate medications. He has smoked a pack of cigarettes daily for 30 years and used intravenous drugs in the past. The patient is treated empirically with a proton pump inhibitor; upper gastrointestinal endoscopy does not reveal a source for the pain or bleeding. Symptoms resolve without further intervention, and he is discharged. Several weeks later, the patient returns to the emergency department with fever, weight loss, and muscle pain. After initial evaluation, muscle biopsy demonstrates transmural inflammation of medium-sized arteries with areas of amorphous, eosin-staining arterial wall necrosis. Areas of disruption of the internal elastic lamina are also present. Which of the following is the most likely predisposing factor for this patient's current condition?
A) Antibiotic use
B) Asthma
C) Hypertriglyceridemia
D) Smoking
E) Viral hepatitis
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 56-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department after a generalized tonic-clonic seizure witnessed by her husband. The patient has no history of seizures or other medical conditions but has been having recurrent headaches for the past several months. Physical examination shows mild weakness with increased deep tendon reflexes in the left upper extremity. MR imaging of the brain reveals a large mass in the right frontal lobe. Stereotactic biopsy of the mass yields hypercellular white matter with extensive astrocytic aberration, microvascular proliferation, and areas of necrosis lined by tumor cells. Molecular studies of the abnormal cells are most likely to demonstrate which of the following findings?
A) Abnormal tuberin and hamartin proteins
B) Constitutively active RET protein
C) Lack of merlin tumor suppressor protein
D) Overexpression of epidermal growth factor receptor
E) Presence of Epstein-Barr virus genome
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 26-year-old woman, gravida 2 para 1, at 8 weeks gestation comes to the office due to pain and swelling of her left leg for the past day. The patient had a pulmonary embolism during her previous pregnancy, and prophylactic low-molecular-weight heparin therapy was initiated 6 days ago. She has no other medical conditions and takes prenatal vitamins. Physical examination shows left lower extremity edema and calf tenderness but no other abnormalities. Venous duplex ultrasonography reveals acute left femoral vein thrombosis. Platelet count, which was normal prior to anticoagulant therapy initiation, is 84,000/mm3. Other blood cell counts and renal and liver function studies are within normal limits. Which of the following most likely predisposed this patient to her current condition?
A) Acquired protein C deficiency
B) Anti-platelet factor 4/heparin antibodies
C) Anti-platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antibodies
D) Cold-precipitable immunoglobulins
E) Decreased ADAMTS13 level
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 29-year-old woman comes to the office due to an intermittent nipple discharge for the past several weeks. She has had no fever or breast pain. The patient has never been pregnant despite having unprotected intercourse. She experienced menarche at age 12. Beginning a year ago, the patient's menses slowed to 2- to 3-month intervals and stopped completely 6 months ago. She has no other medical conditions and takes no medications. The patient's mother was diagnosed with metastatic breast cancer at age 60 and died recently. BMI is 31 kg/m2. On physical examination, white discharge is expressible from both nipples. The remainder of the physical examination is within normal limits. Urine β-hCG testing is negative. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
A) Fibroadenoma
B) Fibrocystic changes of the breast
C) Galactocele
D) Inflammatory breast carcinoma
E) Intraductal papilloma
F) Lobular breast carcinoma
G) Paget disease of the breast
H) Pituitary adenoma
J) A) and H)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 78-year-old man dies of advanced esophageal cancer. The man's family donates his body for teaching purposes and an autopsy is performed. Gross examination of the heart reveals left ventricular chamber size and wall thickness within normal limits. No significant atherosclerosis is seen in the coronary arteries. On microscopic examination, myocardial cells demonstrate prominent yellow-brown intracytoplasmic granules as shown in the exhibit.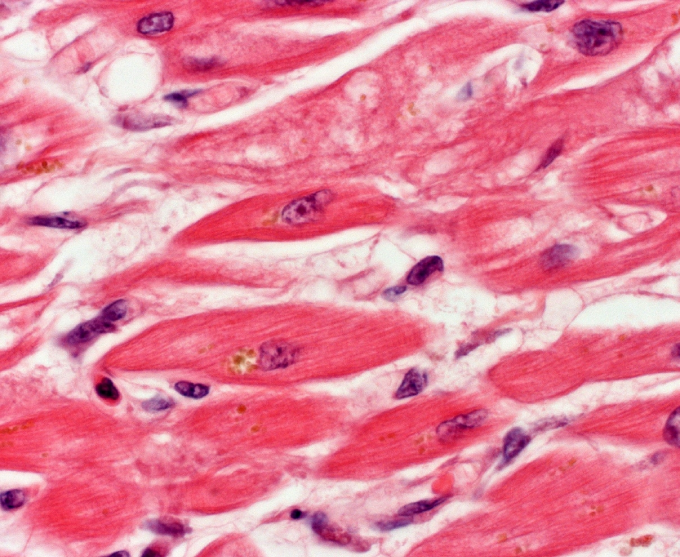 Which of the following most likely accounts for the observed microscopic changes?
Which of the following most likely accounts for the observed microscopic changes?
A) Exogenous pigment endocytosis
B) Glucose polymerization
C) Iron overload
D) Lipid peroxidation
E) Protein accumulation
F) Tyrosine oxidation
H) C) and F)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 36-year-old man comes to the emergency department after briefly losing consciousness while watching television half an hour ago. The patient had no preceding chest pain or shortness of breath, but he has been having recurrent palpitations over the past several days. Two weeks ago, he noticed a non-itchy rash on his thigh that he treated with an over-the-counter steroid cream. Medical history is otherwise unremarkable. There is no family history of heart disease or sudden cardiac death. The patient recently began working as a forest ranger in Pennsylvania. He does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg and pulse is 46/min. The lungs are clear on auscultation and heart sounds are normal. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. ECG reveals complete atrioventricular block. Echocardiography shows normal ventricular function with no major valvular disease. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's current condition?
A) Disseminated spirochetal infection
B) Granulomatous myocardial inflammation
C) Missense mutation of a sarcomere protein
D) Myocyte potassium channel mutation
E) Viral infection-induced cardiac injury
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 42-year-old man comes to the office due to hematuria, fatigue, and nasal congestion for the last few weeks. He has no chronic medical conditions. Blood pressure is 160/96 mm Hg. Physical examination shows edema around the ankles, hands, and face. Laboratory results reveal blood urea nitrogen of 40 mg/dL and serum creatinine of 3.8 mg/dL. Urinalysis shows moderate proteinuria and a large amount of red blood cells (RBCs) with RBC casts. A kidney biopsy is performed. Light microscopy reveals cellular proliferation, focal necrosis, and crescent formation of most of the glomeruli. On immunofluorescent microscopy, there are no immunoglobulin or complement deposits. Which of the following additional findings is most likely to be present in this patient?
A) Decreased serum C3 level
B) Decreased serum C4 level
C) Serum antiglomerular basement membrane antibodies
D) Serum antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies
E) Serum antiphospholipid antibodies
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 42-year-old woman is brought to the hospital due to right-sided weakness and difficulty speaking. She has a longstanding history of a diastolic murmur, but her medical follow-up has been poor. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. A CT scan of the brain reveals a large ischemic stroke involving the left middle cerebral artery distribution. The patient dies 2 days later due to progressive neurologic deterioration. At autopsy, exploration of the left atrium shows diffuse fibrous thickening and distortion of the mitral valve leaflets, commissural fusion at the leaflet edges, and narrowing of the mitral valve orifice. This finding is most likely the result of which of the following conditions?
A) Congenital heart disease
B) Degenerative valvular calcinosis
C) Infective endocarditis
D) Late syphilis
E) Rheumatic fever
F) Rheumatoid arthritis
G) Rupture of the papillary muscle
I) C) and G)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 13-year-old boy is brought to the office for a new patient visit. The patient recently immigrated to the United States with his family. He has no history of significant illness, trauma, or surgery. Physical examination shows Tanner stage IV genitalia but an empty right scrotal sac. A round mass can be palpated in the right inguinal canal. Biopsy of the mass shows marked fibrotic changes with prominent Leydig cells and hypoplastic Sertoli cells. The patient's parents are advised that the mass should be removed. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for the need for surgery in this patient?
A) Maintain adequate function of the contralateral organ
B) Preserve virilization
C) Prevent recurrent infections
D) Reduce the risk of future infertility
E) Reduce the risk of malignancy
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 50-year-old man is brought to the emergency department due to chest pain. He passed out briefly after the pain started. Medical history includes hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and early-stage chronic kidney disease. The patient reports that his father had a heart attack at a young age. Despite treatment, the patient dies during hospitalization. An autopsy is performed. Light microscopy of the aortic wall is shown on the slide below. 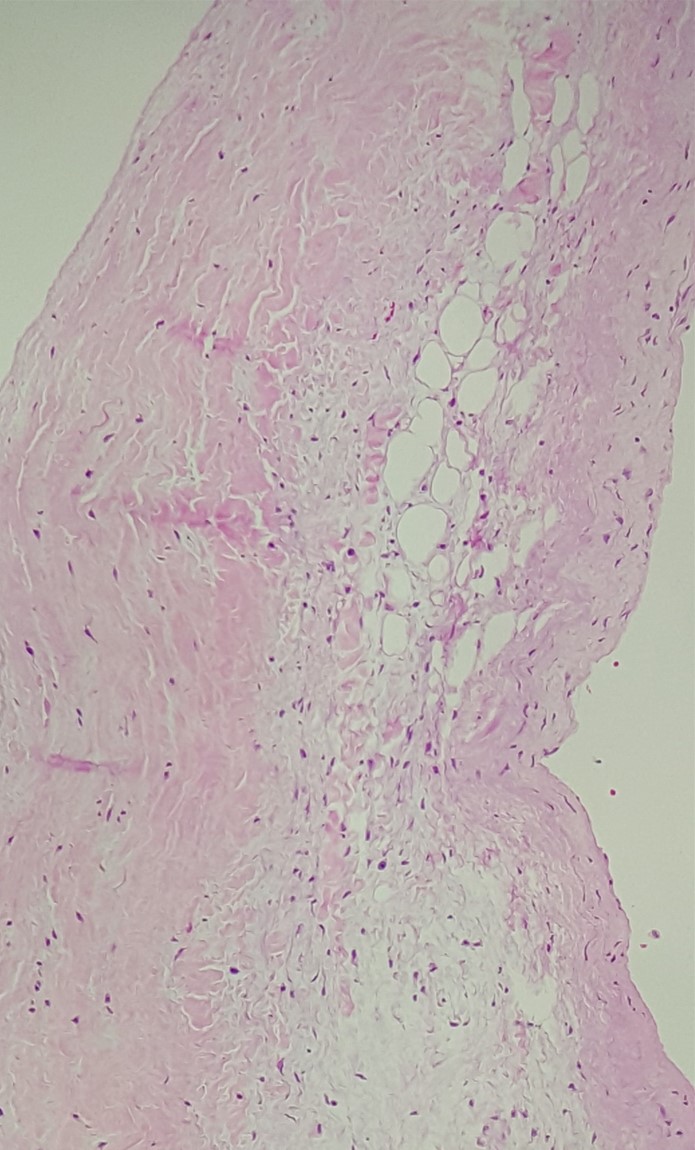 Which of the following underlying mechanisms is most likely responsible for this patient's disease process?
Which of the following underlying mechanisms is most likely responsible for this patient's disease process?
A) Atherosclerosis
B) Calciphylaxis
C) Cystic degeneration of the media
D) Granulomatous inflammation
E) Monckeberg sclerosis
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The cells identified by the special immunohistochemical stain are shown to overexpress a 185 kD glycoprotein that spans the cell membrane and has tyrosine kinase activity in the intracellular domain. Which of the following is the most likely function of this protein?
A) Accelerates cell proliferation
B) Acts as a sex hormone receptor
C) Governs intercellular binding
D) Induces cytokine release
E) Mediates endocytosis
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 381 - 400 of 816
Related Exams