Correct Answer
True/False
Most reabsorption occurs in the distal convoluted tubule.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Podocytes are located in the wall of
A) the Bowman's capsule.
B) the glomerulus.
C) the peritubular capillaries.
D) the renal artery.
E) the proximal convoluted tubule.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Matching
Match the waste product with its description or the animal that excretes it.
Correct Answer
Multiple Choice
The major function of the protonephridia in the flatworm is to
A) conserve water.
B) conserve salts.
C) eliminate waste materials such as ammonia and urea.
D) eliminate excess water.
E) regulate the pH of the gastrovascular cavity.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Matching
Match the term below with its definition/description.
Correct Answer
Multiple Choice
Which statement is accurate of filtration by the kidneys?
A) About 25% of the plasma passing through the glomerulus becomes part of the glomerular filtrate.
B) Solutes dissolved in the plasma such as HDL and globular proteins become part of the filtrate.
C) The normal glomerular filtration rate adds up to about 180 L every 24 hours.
D) Approximately 75% of the filtrate is reabsorbed into the blood through the renal tubules.
E) The filtration membrane prevents the passage of cells, but allows large molecules to pass through.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 48-1
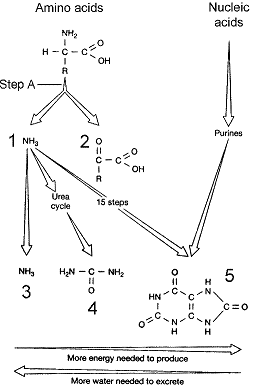
Which structure in the accompanying figure represents the nitrogenous waste urea?
Which structure in the accompanying figure represents the nitrogenous waste urea?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The main difference between protonephridia and metanephridia is that
A) protonephridia are involved in osmoregulation, whereas metanephridia are involved in excretion.
B) protonephridia consist of blind flame cells, whereas metanephridia consist of tubules open at both ends.
C) protonephridia are involved in excretion, whereas metanephridia are involved in osmoregulation.
D) protonephridia consist of tubules open at both ends, whereas metanephridia consist of blind flame cells.
E) protonephridia are found in annelids and metanephridia are found in flatworms.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The efferent arterioles transport blood directly into the
A) afferent arterioles.
B) Bowman's capsule.
C) glomerulus.
D) peritubular capillaries.
E) renal artery.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Matching
Match the term below with its definition/description.
Correct Answer
Showing 101 - 111 of 111
Related Exams