A) A p* antibonding molecular orbital is formed when two p orbitals of similar phase overlap.
B) A p* antibonding molecular orbital is formed when two p orbitals of opposite phase overlap.
C) A p* antibonding molecular orbital is a higher-energy molecular orbital than a p bonding molecular orbital.
D) Both the statements a p* antibonding molecular orbital is formed when two p orbitals of opposite phase overlap and a p* antibonding molecular orbital is a higher-energy molecular orbital than a p bonding molecular orbital are true.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the major organic product of the following Claisen rearrangement? 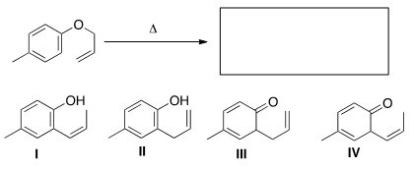
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the correct classification of the following reaction? 
A) Cycloaddition reaction
B) Electrophilic reaction
C) Electrocyclic reaction
D) Sigmatropic reaction
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about orbital symmetry and cycloaddition reactions is true?
A) Thermal cycloadditions involving an even number of p bonds proceed by a suprafacial pathway.
B) Thermal cycloadditions involving an odd number of p bonds proceed by a suprafacial pathway.
C) Photochemical cycloadditions involving an odd number of p bonds proceed by a suprafacial pathway.
D) Photochemical sycloadditions involving an even number of p bonds proceed by an antarafacial pathway.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about cycloaddition reactions is true?
A) Cycloaddition reactions can be initiated by heat only.
B) Cycloaddition reactions can be initiated by light only.
C) Cycloaddition reactions can be initiated by heat or light.
D) Cycloaddition reactions are identified by the number of p electrons in the two products.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about cycloaddition reactions is not true?
A) Cycloaddition reactions form a cyclic product with two new s bonds.
B) The course of the reaction is determined by the symmetry of the molecular orbitals of the products.
C) Cycloaddition reactions are concerted.
D) Cycloaddition reactions are stereospecific.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about thermal electrocyclic reactions is not true?
A) The number of s bonds in the conjugated polyene determines whether rotation is conrotatory or disrotatory.
B) Thermal electrocyclic reactions occur in a disrotatory fashion for a conjugated polyene with an odd number of p bonds.
C) Thermal electrocyclic reactions occur in a conrotatory fashion for a conjugated polyene with an even number of p bonds.
D) In thermal reactions,we consider the orbitals of the HOMO of the ground state electronic configuration to determine the course of the reaction.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Predict the major organic product(s) of the following electrocyclic reaction. 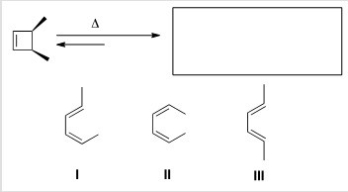
A) Only I
B) Only II
C) Only III
D) Only I and II
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about photochemical electrocyclic reactions is not true?
A) In photochemical reactions,we consider the orbitals of the HOMO of the excited state to determine the course of the reaction.
B) Photochemical electrocyclic reactions occur in a conrotatory fashion for a conjugated polyene with an odd number of p bonds.
C) Photochemical electrocyclic reactions occur in a disrotatory fashion for a conjugated polyene with an even number of p bonds.
D) In photochemical reactions,we consider the orbitals of the LUMO of the excited state to determine the course of the reaction.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the correct classification of the following reaction? 
A) Cycloaddition reaction
B) Electrophilic reaction
C) Electrocyclic reaction
D) Sigmatropic reaction
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following reaction sequence.What is the correct classification of the first reaction in the sequence? ![Consider the following reaction sequence.What is the correct classification of the first reaction in the sequence? A) [1,3] Sigmatropic rearrangement B) [1,5] Sigmatropic rearrangement C) [3,3] Sigmatropic rearrangement D) [5,5] Sigmatropic rearrangement](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7662/11eac43c_f778_2773_a9af_b3429e317bc5_TB7662_00.jpg)
A) [1,3] Sigmatropic rearrangement
B) [1,5] Sigmatropic rearrangement
C) [3,3] Sigmatropic rearrangement
D) [5,5] Sigmatropic rearrangement
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about an electrocyclic ring-opening reaction is not true?
A) An electrocyclic ring-opening reaction is an intramolecular reaction.
B) An electrocyclic ring-opening reaction requires a source of energy (heat or light) .
C) The product of an electrocyclic ring-opening reaction contains one fewer p bond than the reactant.
D) The product of an electrocyclic ring-opening reaction contains one more p bond than the reactant.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about pericyclic reactions is not true?
A) Pericyclic reactions are concerted reactions.
B) Pericyclic reactions proceed through a cyclic transition state.
C) Pericyclic reactions are not stereospecific.
D) Pericyclic reactions require light or heat.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about a p-bonding molecular orbital is true?
A) A p-bonding molecular orbital is formed when two p orbitals of similar phase overlap.
B) A p-bonding molecular orbital is lower in energy than a s-bonding molecular orbital.
C) A p-bonding molecular orbital is formed when two p orbitals of opposite phase overlap.
D) Both the statements a p-bonding molecular orbital is formed when two p orbitals of similar phase overlap and a p-bonding molecular orbital is lower in energy than a s-bonding molecular orbital are true.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Predict the major organic product(s) of the following electrocyclic reaction. 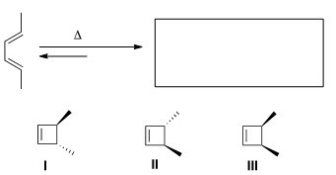
A) Only I
B) Only II
C) Only III
D) Only I and II
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What are the two modes of bond formation in cycloaddition reactions?
A) Suprafacial and antarafacial bond formations
B) Superfacial and antifacial bond formations
C) Suprafacial and synfacial bond formations
D) Synfacial and antifacial bond formations
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about sigmatropic reactions is not true?
A) A sigmatropic reaction is an intramolecular pericyclic reaction.
B) In a sigmatropic reaction,s bond is broken in one of the reactants.
C) The p bonds rearrange in a sigmatropic reaction.
D) The number of p bonds in the reactants and product differs in a sigmatropic reaction.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Predict the major organic product(s) of the following electrocyclic reaction. 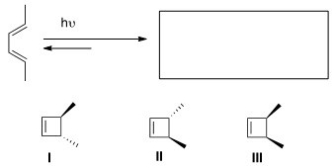
A) Only I
B) Only II
C) Only III
D) Only I and II
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following reaction sequence.What is the correct classification of the second reaction in the sequence? ![Consider the following reaction sequence.What is the correct classification of the second reaction in the sequence? A) [2 + 2] Cycloaddition B) [6 + 4] Cycloaddition C) [4 + 4] Cycloaddition D) [4 + 2] Cycloaddition](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7662/11eac43c_f778_7594_a9af_c74a5759c8b4_TB7662_00.jpg)
A) [2 + 2] Cycloaddition
B) [6 + 4] Cycloaddition
C) [4 + 4] Cycloaddition
D) [4 + 2] Cycloaddition
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of sigmatropic rearrangement is illustrated below? ![What type of sigmatropic rearrangement is illustrated below? A) [1,3] B) [1,4] C) [3,3] D) [1,5]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7662/11eac43c_f776_a0ce_a9af_bfcaf763f9a1_TB7662_00.jpg)
A) [1,3]
B) [1,4]
C) [3,3]
D) [1,5]
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 62
Related Exams